Email Channel
The Email Channel allows the helpdesk system to receive and process tickets from email communications. This integration enables seamless ticket creation from incoming emails and provides a complete email management solution within the ticketing system.
Connection Setup
Basic Configuration
-
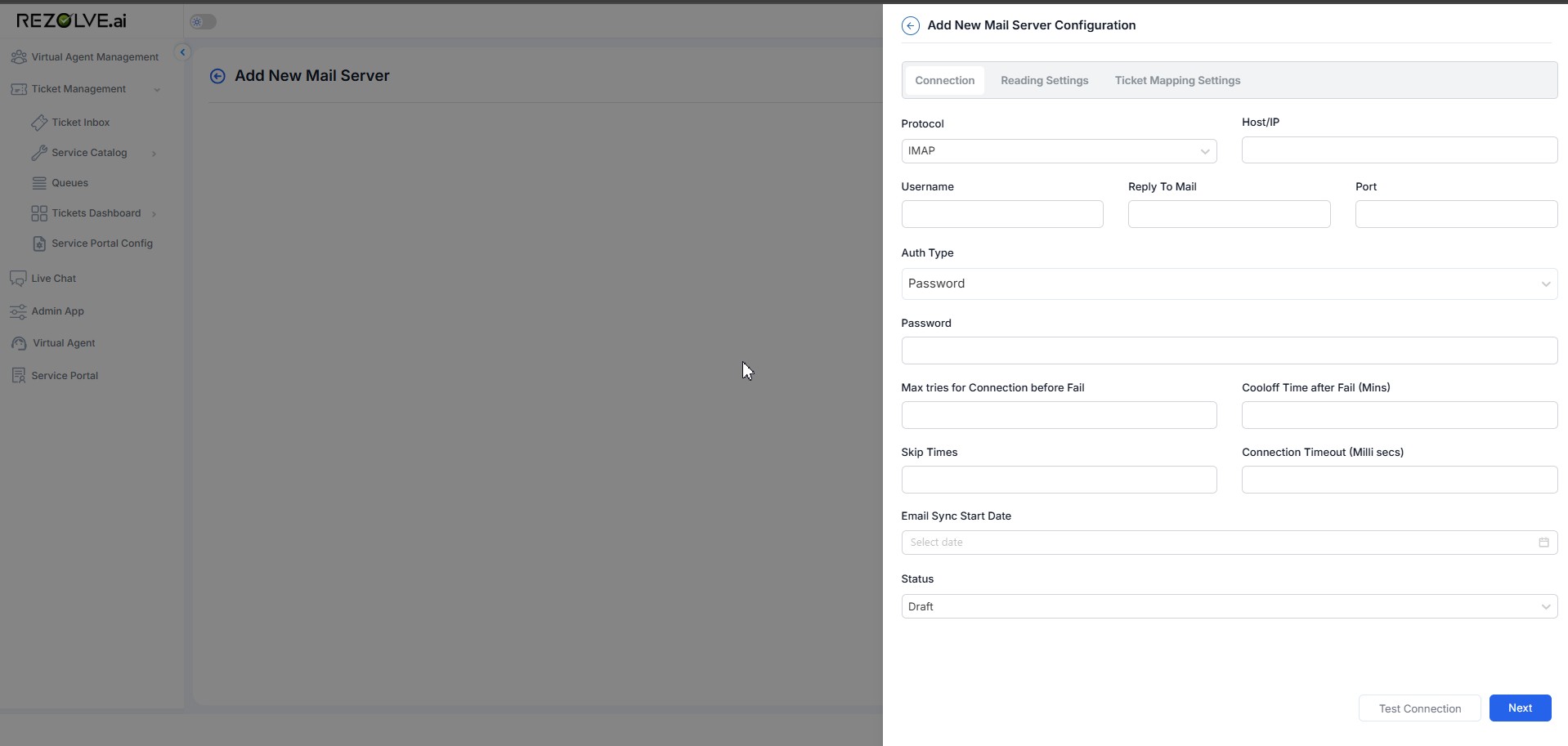
Protocol
- Description: Specifies the email protocol to be used for communication.
- Options: IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol)
- Expected Input: Select "IMAP" from the dropdown.
-
Host/IP
- Description: The mail server's hostname or IP address.
- Expected Input: A valid domain name (e.g., mail.example.com) or an IP address (e.g., 192.168.1.1).
-
Username
- Description: The email account username used for authentication.
- Expected Input: A valid email address or username associated with the mail server.
-
Reply To Mail
- Description: The email address where replies should be sent.
- Expected Input: A valid email address (e.g., support@example.com).
-
Port
- Description: The port number used for IMAP communication.
- Expected Input: Numeric values such as 993 (for IMAPS) or 143 (for IMAP).
-
Auth Type
- Description: Specifies the authentication method for the email server.
- Expected Input: Select from available authentication types such as Password-based Authentication or OAuth.
OAuth Configuration (If OAuth is Selected)
-
Azure Active Directory Tenant ID
- Description: The unique identifier for the Azure Active Directory tenant.
- Expected Input: A valid Tenant ID from Azure AD (e.g., a GUID-like string).
-
Redirect URL
- Description: The URL to which the authentication service will redirect after successful authentication.
- Expected Input: A valid URL (e.g., https://yourdomain.com/callback).
-
Refresh Token
- Description: A token used to obtain a new access token when the current one expires.
- Expected Input: A valid refresh token provided during OAuth setup.
-
Client ID
- Description: The unique identifier assigned to the application in Azure AD.
- Expected Input: A valid Client ID obtained from the Azure AD application registration.
-
Client Secret
- Description: A secret key used to authenticate the application with the OAuth provider.
- Expected Input: A securely stored client secret from Azure AD.
-
Scope
- Description: The permissions requested by the application when accessing the mail server.
- Expected Input: A valid OAuth scope (e.g., https://outlook.office365.com/.default).
-
Token Endpoint
- Description: The URL used to obtain an access token from the OAuth provider.
- Expected Input: A valid token endpoint URL (e.g., https://login.microsoftonline.com/{tenant_id}/oauth2/token).
Password Authentication (If Selected)
- Password
- Description: The password associated with the specified email account.
- Expected Input: A secure password that matches the username provided.
- Security Note: Ensure the password is stored securely and not exposed in logs.
Connection Settings
-
Max Tries for Connection Before Fail
- Description: The maximum number of attempts before marking the connection as failed.
- Expected Input: A numeric value (e.g., 3 for three attempts).
-
Cool-off Time After Fail (Minutes)
- Description: The waiting time before retrying a failed connection.
- Expected Input: A numeric value representing minutes (e.g., 5 for five minutes).
-
Skip Times
- Description: Specifies time intervals to skip connection attempts.
- Expected Input: Time intervals in a specific format (e.g., 02:00-04:00).
-
Connection Timeout (Milliseconds)
- Description: The maximum time the system waits for a connection response before timing out.
- Expected Input: A numeric value in milliseconds (e.g., 5000 for 5 seconds).
-
Email Sync Start Date
- Description: The starting date from which emails should be synchronized.
- Expected Input: A valid date selection.
-
Status
- Description: Defines the current configuration status.
- Options: Draft, Active, etc.
- Expected Input: Select the appropriate status from the dropdown.
-
Test Connection
- Description: A button to validate the entered configuration details.
- Expected Input: Click to verify if the connection is successful.
-
Next Button
- Description: Proceeds to the next step in the configuration process.
- Expected Input: Click to navigate forward after entering all required fields.
Reading Settings
-
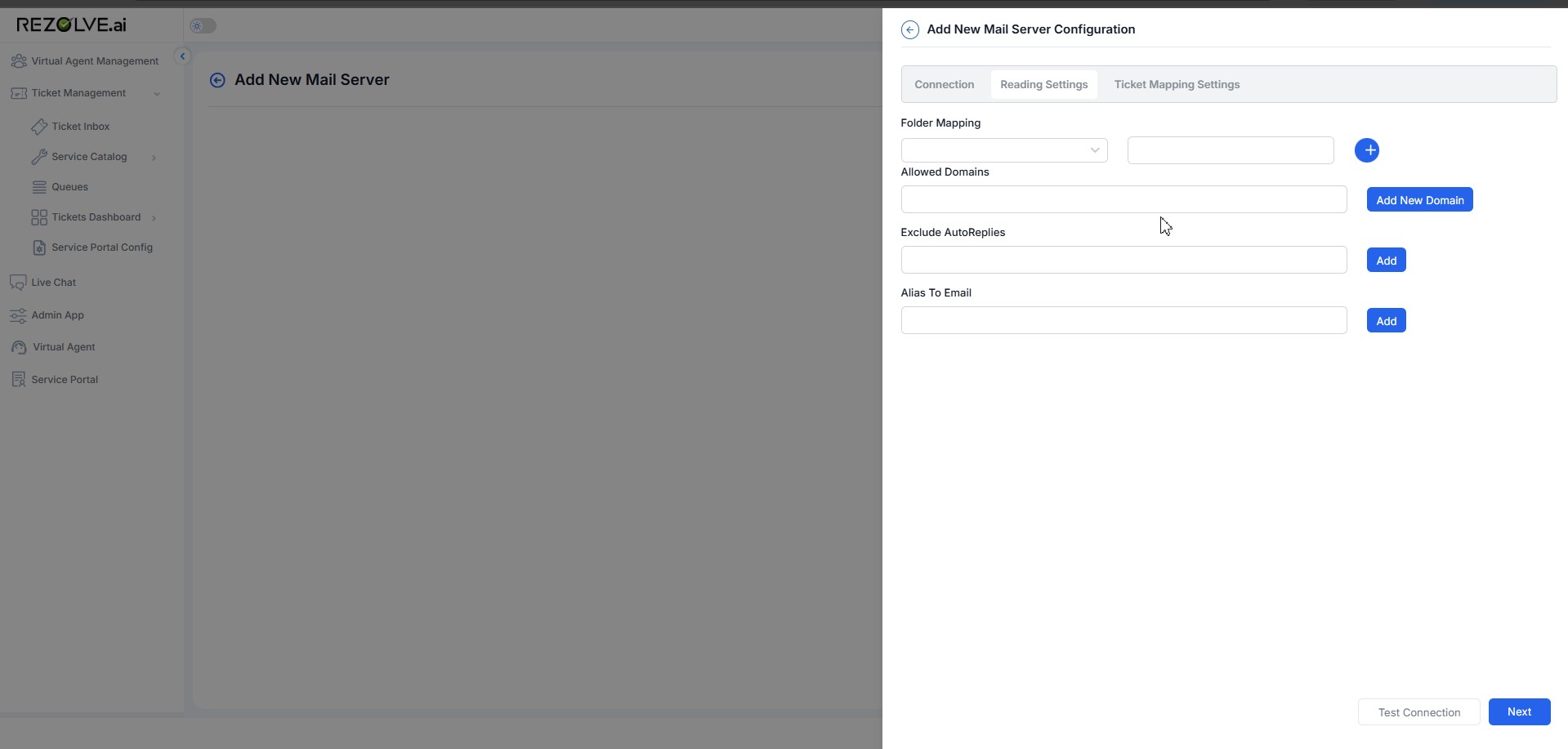
Folder Mapping
- Purpose: Specifies the email folder from which the system should retrieve emails (e.g., "Inbox," "Support Requests").
- Input: Select the folder from the dropdown or enter a custom folder name.
-
Allowed Domains
- Purpose: Restricts email processing to messages sent from specific domains.
- Input: Enter one or multiple domains (e.g., company.com, support.com).
-
Exclude Auto-Replies
- Purpose: Filters out automatic email responses like out-of-office replies.
- Input: Enter keywords or specific sender addresses to exclude such emails.
-
Alias to Email
- Purpose: Maps alternative email addresses to a primary one for ticket processing.
- Input: Enter an alias email address.
Ticket Mapping Settings
-
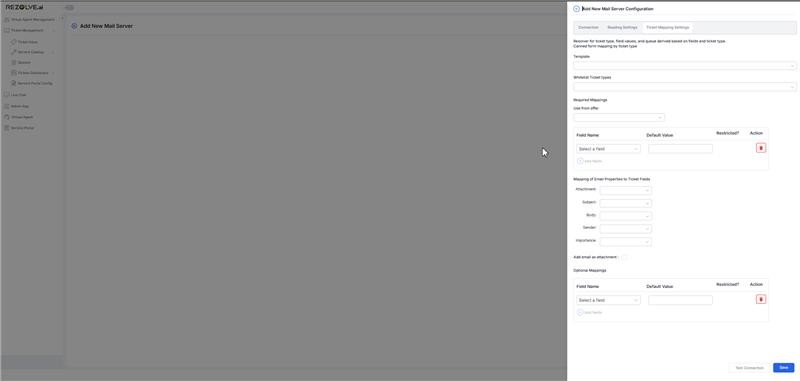
Template
- Purpose: Defines published templates within the tenant.
- Input: Select a template from the dropdown list.
-
Whitelist Ticket Types
- Purpose: Restricts processing to specific ticket types.
- Input: Choose from the dropdown.
-
Required Mappings
- Use from Offer: Select an offer to create a default mail server offer.
-
Custom Field Mappings
- Field Name: Lists only required fields of the selected template.
- Default Value: Set a fallback value if no corresponding email data exists.
- Restricted?: Determines if field access is limited to specific roles.
- Action: Option to remove mapping.
-
Mapping Email Properties to Ticket Fields
- Attachment: Determines how email attachments are handled.
- Subject: Maps email subject to a ticket field.
- Body: Maps email body to a ticket field.
- Sender: Identifies and maps sender's email.
- Importance: Maps email priority (High, Medium, Low).
-
Add Email as Attachment
- Purpose: Enables attaching the entire email to a ticket.
- Input: Checkbox to enable or disable.
-
Optional Mappings
- Field Name: Additional fields for mapping.
- Default Value: Assigned value if missing in the email.
- Restricted?: Limits access based on roles.
- Action: Option to remove mapping.
Final Actions
- Test Connection: Validates the settings before saving.
- Save: Confirms and stores the configurations.
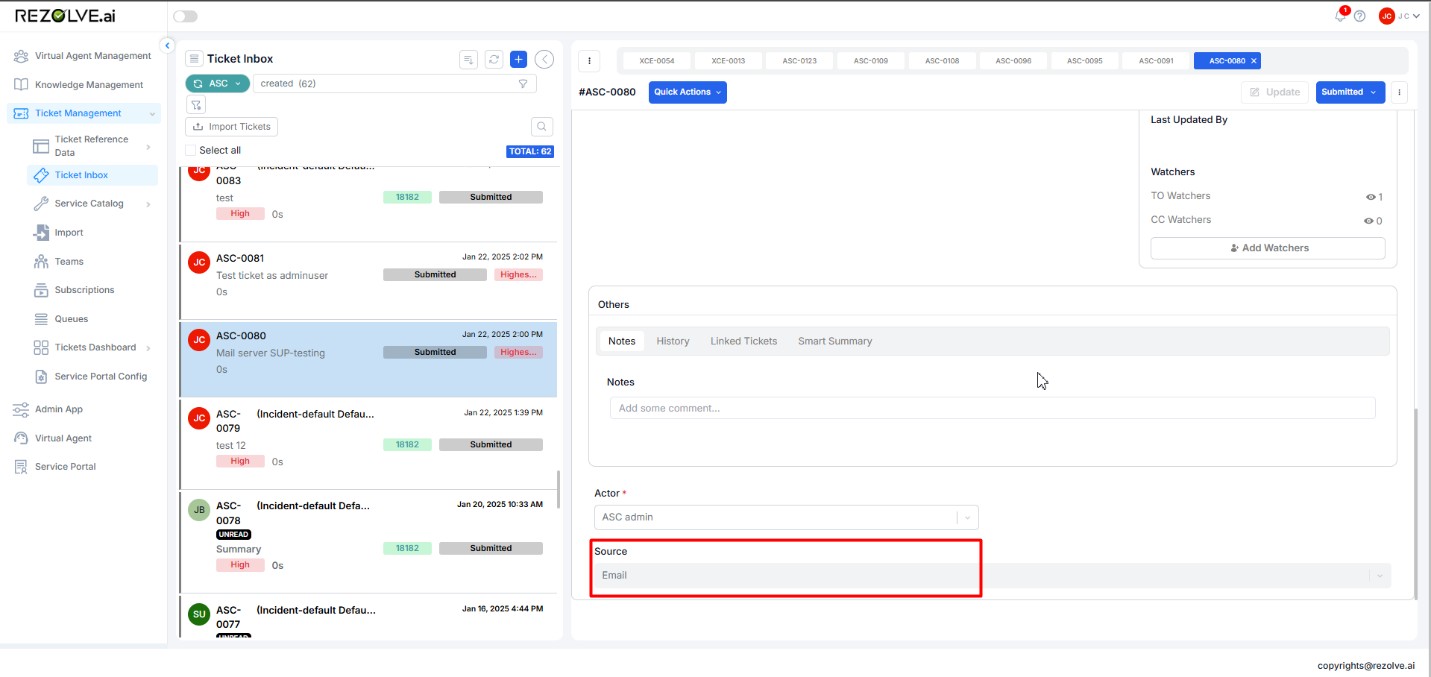
Ticket Creation from Email
- Purpose: Automatically generates a ticket when an end user sends an email.
- Input: When an email is received from a configured email source, the system creates a ticket and marks its source as "Email," as shown in the provided screenshot.
- Configuration Dependency: Ensure the mail server is correctly set up to receive and process emails.
Best Practices for Email Channel Configuration
-
Security Considerations
- Use OAuth authentication when possible for enhanced security
- Regularly rotate credentials and tokens
- Implement IP restrictions if supported by your mail server
-
Performance Optimization
- Set appropriate connection timeout values to prevent system slowdowns
- Configure reasonable retry intervals for failed connections
- Use folder mapping effectively to process only relevant emails
-
Email Processing
- Create clear rules for auto-reply exclusion to prevent ticket duplication
- Set up domain filtering to reduce spam tickets
- Configure proper field mappings to ensure accurate ticket information
-
Maintenance
- Regularly test the email connection to ensure proper functionality
- Monitor the email channel for any issues or performance degradation
- Update configurations when mail server settings change