Overview
Rezolve.ai implements a sophisticated organizational structure through Teams and Queues that enables efficient work distribution, specialized handling of different request types, and appropriate access controls. This two-tier organizational framework provides flexibility and precision in managing support operations across different departments and functions.
Teams represent broad organizational units or departments (like IT, HR, Facilities, etc), while Queues operate as specialized work distribution channels within those teams. This hierarchical arrangement allows for both high-level organizational alignment and granular work assignment capabilities, creating an efficient system for handling diverse support needs.
Team Configuration
Initial Team Setup
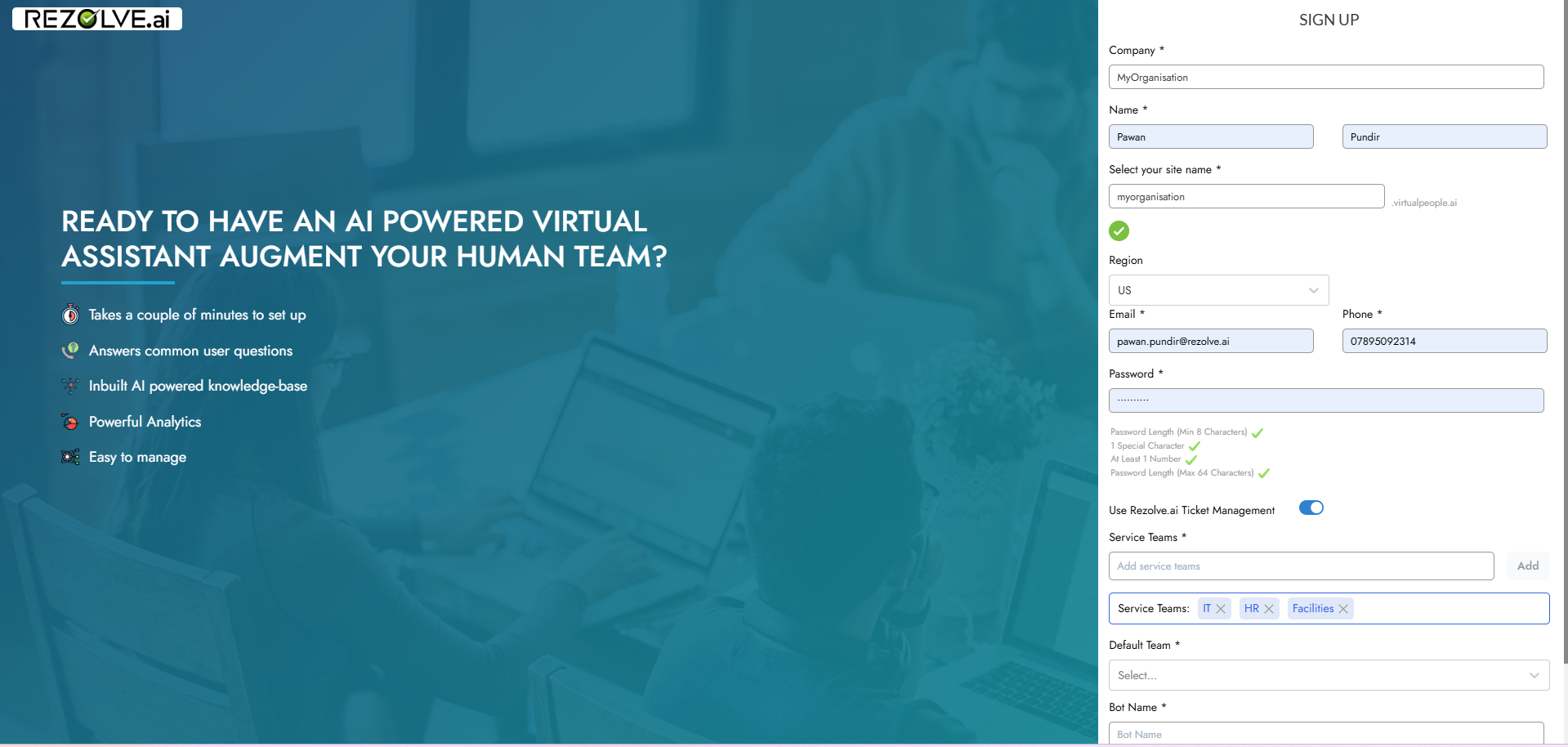
Teams are initially defined during the tenant registration process:
- During tenant setup, administrators specify which functional teams will be using the system
- Common team designations include IT, HR, Facilities, Finance, and other organizational departments
- These core teams become the foundation of the organizational structure within Rezolve.ai
- The specification of teams during registration ensures the system is immediately aligned with organizational structure
Adding Teams Post-Registration
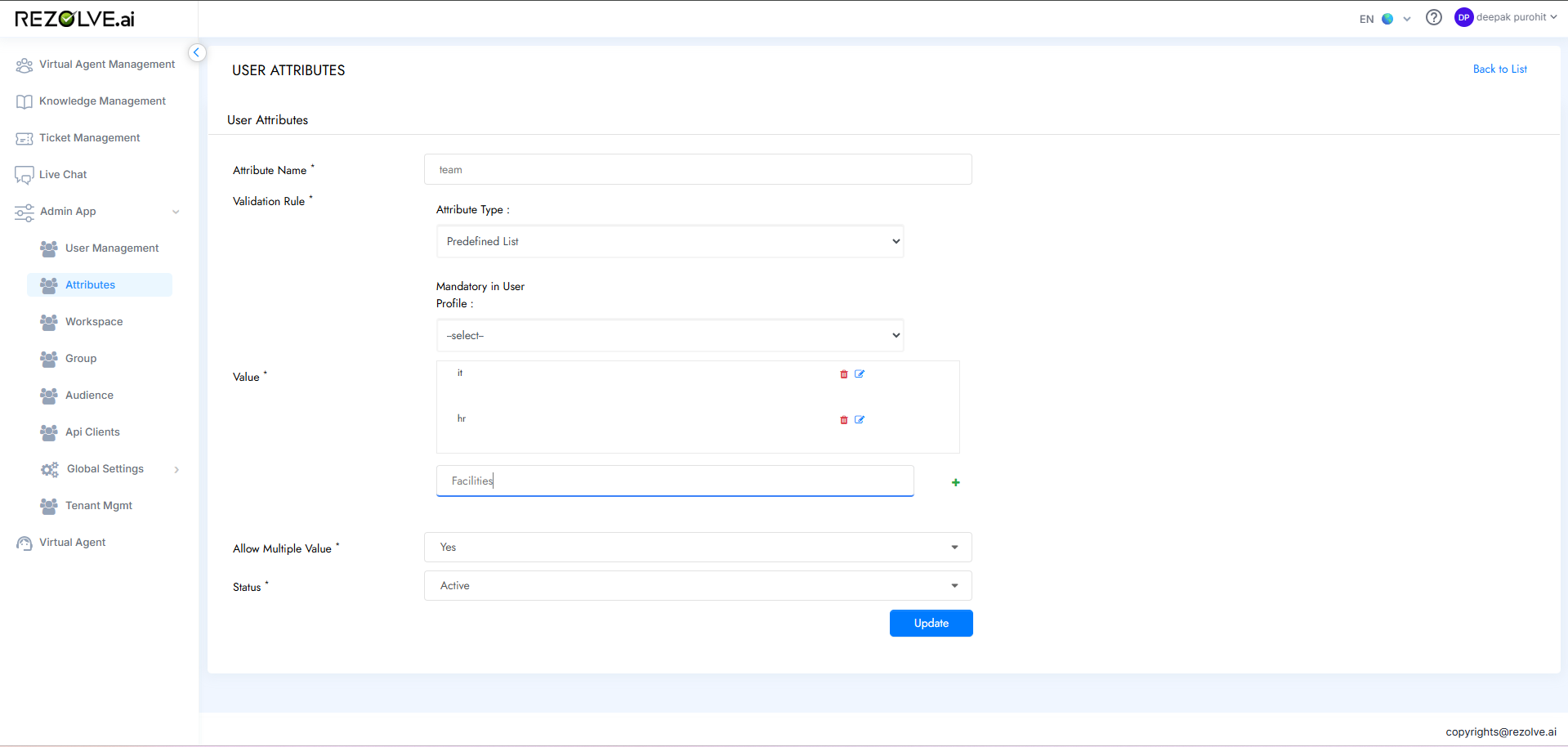
After initial setup, tenant administrators can expand the team structure as needed:
- Navigate to the Admin App
- Access the Attributes section
- Edit the team attributes
- Configure the new teams with appropriate settings and descriptions
- Save the new team configurations
This flexibility allows the organizational structure to evolve as the organization grows or reorganizes, ensuring the Rezolve.ai implementation remains aligned with current business realities.
Queue Configuration
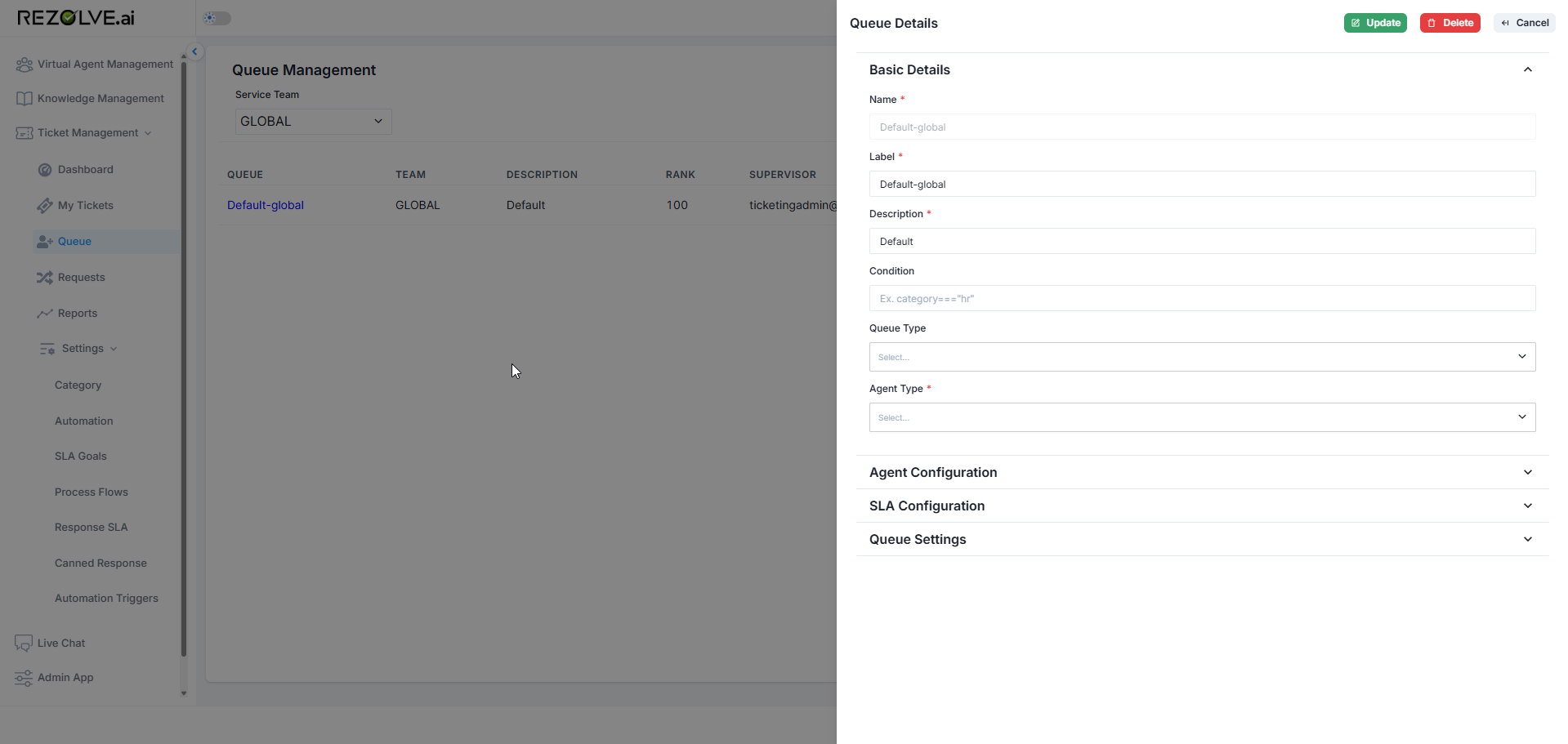
Default Queue Creation
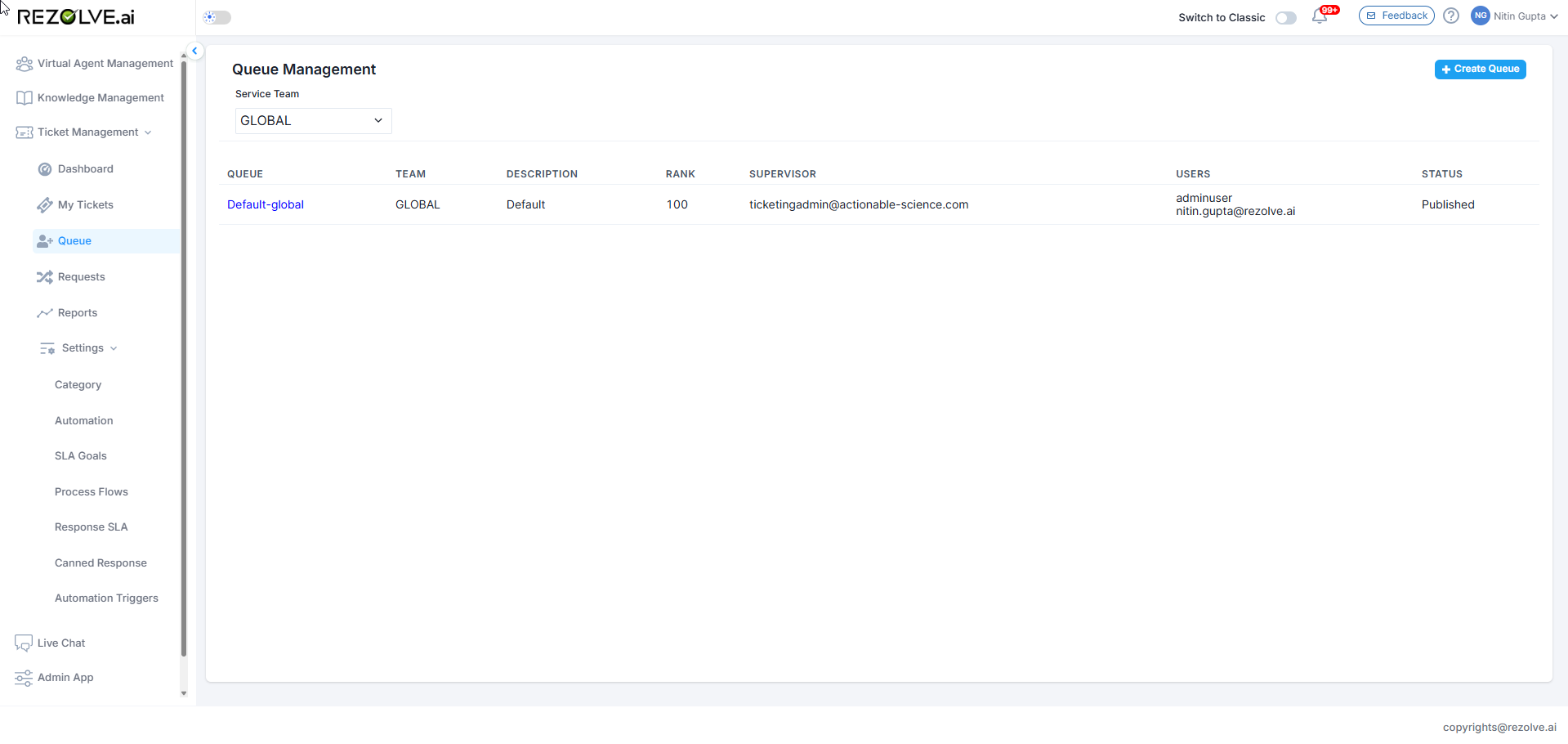
For each team defined in the system, Rezolve.ai automatically creates a default queue:
- When a team is created (either during registration or later), a default queue is generated
- The default queue shares the team's name (e.g., "Default IT Queue" for the IT team)
- This default queue serves as the primary work distribution channel for that team
- The automatic creation ensures immediate operational capability for each team
Custom Queue Creation
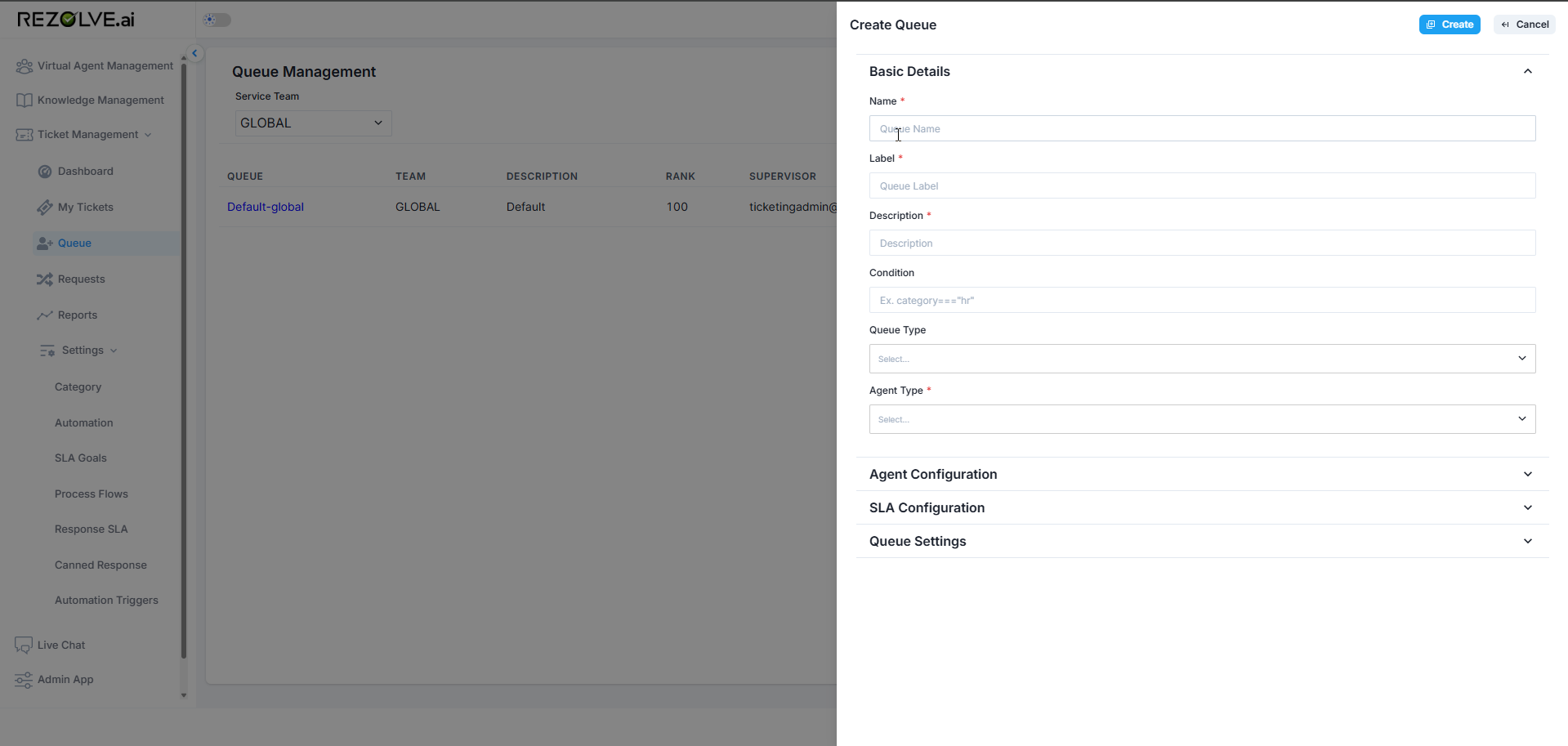
Beyond default queues, administrators can create multiple custom queues for each team to address specific business needs:
- Navigate to the Queue Management interface
- Select "Create New Queue" or similar option
- Provide a descriptive name for the queue
- Select the parent team for this queue
- Configure queue-specific settings
- Assign queue supervisors and members
- Establish routing rules if applicable
- Save the queue configuration
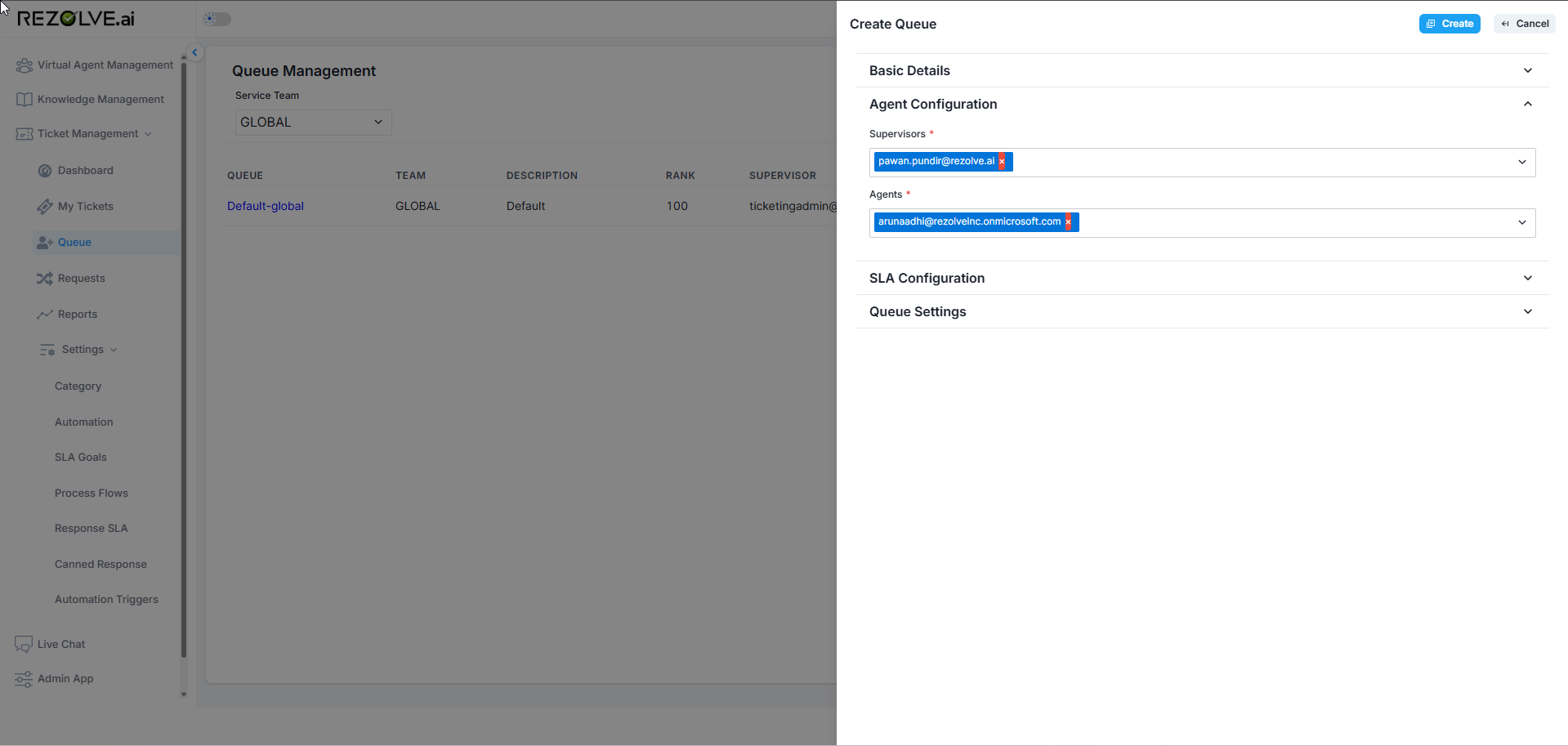
Custom queues allow organizations to create specialized handling paths for different types of requests, expertise areas, or priority levels within a team.
Queue Membership
Queues require proper staffing to function effectively:
Queue Supervisors
- Oversee queue operations and performance
- Have administrative capabilities for the queue
- Can assign and reassign items within the queue
- Monitor queue metrics and team member performance
- Typically senior team members or team leaders
Queue Members
- Handle the actual work items in the queue
- Process tickets or chat requests assigned to them
- May have specific expertise related to the queue's purpose
- Can be members of multiple queues simultaneously
- Receive assignments based on queue routing rules
Functional Applications
Live Chat Operations
Queues play a crucial role in live chat management:
- Chat requests are routed to appropriate queues based on topic, user attributes, or explicit selection
- Queue members with availability receive chat assignments
- Queue supervisors can monitor active chats and assist when needed
- Performance metrics are tracked at both queue and individual levels
- Custom queues allow specialization (technical issues, billing questions, product information)
Ticketing System
The ticketing system heavily leverages the queue structure:
- Tickets are assigned to queues based on routing rules
- Queue members claim tickets or receive assignments
- Work distribution can be balanced across queue members
- Escalation paths often involve movement between queues
- SLAs can be defined at the queue level
- Reporting provides insights into queue performance and workload
Integration with Other Features
Teams and Queues integrate with various Rezolve.ai features:
Knowledge Management
- Knowledge articles can be associated with specific teams/queues using Audience
- Subject matter experts within queues can be responsible for knowledge content
- Usage analytics can show which queues benefit most from knowledge content
Workflow Management
- Different queues may have specialized workflow configurations
- Transitions between workflow states can trigger queue reassignments using Action/Events
- Queue-specific approval processes can be implemented
Analytics and Reporting
- Performance metrics can be analyzed by team and queue
- Workload distribution across queues provides operational insights
- Response times and resolution rates can be compared across queues
Common Queue Configurations
IT Support Example
A typical IT support implementation might include:
- IT Helpdesk Queue: General technical inquiries and first-level support
- Network Support Queue: Network-specific issues requiring specialized knowledge
- Software Queue: Application and software-related problems
- Hardware Queue: Physical device troubleshooting and replacement
- Security Incidents Queue: Security-related concerns requiring immediate attention
HR Department Example
An HR department might structure queues as:
- General HR Queue: Basic policy questions and general inquiries
- Benefits Queue: Benefits-specific questions requiring specialized knowledge
- Onboarding Queue: New employee processing and setup
- Employee Relations Queue: Sensitive interpersonal issues
- Payroll Queue: Compensation and payment issues
Queue Routing and Assignment
Routing Rules
Queues can implement sophisticated routing rules:
- Skill-Based Routing: Directing items to queues based on required expertise
- Load Balancing: Distributing work evenly across appropriate queues
- Priority Routing: High-priority items directed to specialized queues
- Attribute-Based Routing: Using requester attributes to determine appropriate queue
- Content-Based Routing: Analyzing request content to identify the best queue

Assignment Methods
Once items reach a queue, different assignment methods can be employed:
- Manual Assignment: Queue supervisors explicitly assign items to team members
- Self-Assignment: Queue members claim items from a shared pool
- Automatic Assignment: System assigns based on availability and expertise
- Round-Robin: Equal distribution of new items across available team members
- Skill Matching: Assignment based on best match between item needs and agent skills
Best Practices for Teams and Queues
Organizational Design
When designing your team and queue structure:
- Mirror Organizational Structure: Teams should reflect actual departmental divisions
- Create Purpose-Specific Queues: Each queue should have a clear, distinct purpose
- Avoid Queue Proliferation: Create enough queues for effective specialization without unnecessary complexity
- Consider Workload Balance: Design queue structure with workload distribution in mind
- Plan for Scalability: Create a structure that can accommodate growth
Operational Efficiency
To maximize the effectiveness of your queue structure:
- Cross-Training: Ensure multiple team members can handle each queue
- Queue Ownership: Assign clear responsibility for queue performance
- Regular Reviews: Periodically assess queue effectiveness and workload
- Clear Escalation Paths: Define when and how items should move between queues
- Appropriate Staffing: Align queue staffing with volume and complexity expectations
Maintenance and Evolution
To ensure ongoing effectiveness:
- Regular Audits: Periodically review team and queue structures against current needs
- Performance Analysis: Identify underperforming or overloaded queues
- Adjustment Process: Establish procedures for modifying queue structures
- Member Rotation: Consider rotating members across queues for knowledge sharing
- Documentation: Maintain clear documentation of queue purposes and procedures
Implementation Considerations
Setup Planning
Before implementing teams and queues:
- Organizational Analysis: Assess current departmental structure and workflow
- Volume Assessment: Understand typical request volumes by type
- Expertise Mapping: Identify specialized knowledge areas requiring dedicated queues
- Process Documentation: Document current routing and assignment processes
- Future Growth: Consider anticipated organizational changes
Change Management
When implementing or modifying team and queue structures:
- Stakeholder Involvement: Include team members in planning discussions
- Clear Communication: Explain the purpose and benefits of the structure
- Training: Ensure all users understand the new routing and assignment processes
- Phased Implementation: Consider rolling out changes gradually
- Feedback Mechanisms: Collect and act on user feedback about the new structure
Advanced Configurations
Time-Based Routing
For organizations spanning multiple time zones or providing 24/7 support:
- Follow-the-Sun Queues: Different queues active during different time periods
- After-Hours Routing: Special handling for requests outside business hours
- Automatic Handoff: Transitioning unresolved items between time zone teams
Priority-Based Queues
For organizations with varying urgency levels:
- Critical Incident Queues: Dedicated handling for urgent issues
- Standard Request Queues: Normal priority item processing
- Low-Priority Queues: Batch processing of non-urgent requests
Conclusion
The Teams and Queues structure in Rezolve.ai provides a powerful framework for organizing support operations, distributing work effectively, and ensuring requests are handled by the most appropriate resources. By establishing teams that align with organizational departments and creating purpose-specific queues within those teams, organizations can achieve both structural alignment and operational efficiency.
The automatic creation of default queues during tenant registration ensures immediate functionality, while the ability to create custom queues provides the flexibility to address specific business requirements. This balanced approach allows organizations to start with a simple structure and evolve toward greater specialization as needed.
When properly implemented, the Teams and Queues framework creates clear paths for request routing, enables appropriate specialization, facilitates effective workload distribution, and provides meaningful performance metrics at both broad and granular levels. This organizational clarity contributes significantly to the overall effectiveness of support operations and the quality of service delivered to users.